

Individuals with deficits in visuospatial and executive functions typically perform poorly on command and copy conditions. While the command condition requires numerous cognitive functions, the copy condition largely draws upon visuospatial and executive functions.

On a separate sheet, patients then copy a predrawn clock model. As classically defined by Edith Kaplan (1988), clock test administration involves first commanding patients to ‘draw the face of a clock with all the numbers and set the two hands to 10 after 11’. However, it is necessary that the test be administered by a professional, and accompanied by a primary means of diagnosis.Clock drawing is considered particularly beneficial for dementia assessment when both command and copy conditions are used and analyzed for errors.

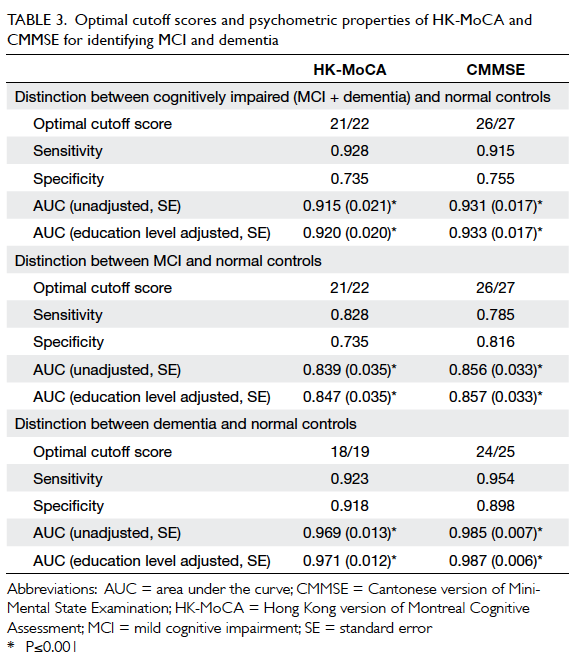
The MoCA has been tested for reliability, and researchers have concluded that the test is a useful and accurate means of detecting mild dementia.
Any score of 25 or less is considered to be an indication of some form of cognitive impairment, which can predict or identify the onset of dementia in patients. The total possible score is 30, with any score higher than 25 considered normal. (5 points) “Orientation" tests a patient's understanding of his current place and the current time.(5 points) “Delayed Recall" forces the recall of the terms read in “Memory," approximately five minutes later.A patient is awarded one point for each commonality he/she can identify. (3 points) The “Abstraction" phase revolves around three pairs of words.(1 point) “Verbal Fluency" tests a patient's vocabulary if 11 or more specific words are spoken (such as words starting with a certain letter), the patient is scored one point.(2 points) “Sentence Repetition" involves two spoken sentences that are repeated: one point is scored for each successful repetition.Three smaller sections involve repeating digits, acknowledging spoken letters, and counting backward from 100 by sevens. (6 points) “Attention" requires a patient to successfully pay attention to verbal commands.(0 points) The first “Memory" section involves no points, and simply involves reading a list of five words to be recalled later.(3 points) The “Naming" phase asks the patient to name each of three common animals, scoring one point for each correct answer.One point each is awarded for having a contour, having numbers, and having hands. (3 points) In the “Visuoconstructional Skills (Clock)" portion, a patient is asked to draw a clock.If a three-dimensional drawing with relatively accurate lines is drawn, the point is awarded. (1 point) The “Visuoconstructional Skills (Cube)" segment relays instructions to copy a drawing of a cube.(1 point) In “Alternating Trail Making," a patient is told to draw a line from letters to numbers, in ascending order (1-A-2-B-3-C-4-D-5-E), without crossing any lines.There are 11 sections of the assessment, with a total of 30 possible points: The test is made freely available to any clinician, and its international use allows it to be administered in 35 different languages. The MoCA is administered over approximately ten minutes, with 30 possible points. The assessments in the test attempt to gauge areas of language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall and abstract thinking, to give a representation of a person's current cognitive ability. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), developed in Canada in 1996, was intended to be a means of accurately detecting levels of cognitive impairment. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment is an accurate test that can give examiners insight into a person's cognitive ability. To detect Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia early on and monitor progression, there are several cognitive evaluations that can assist professionals in a diagnosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
